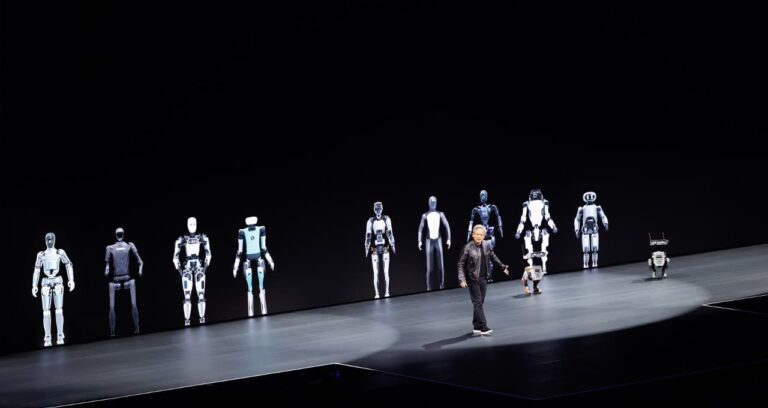
Artificial intelligence has been big this year, and so have the robots that operate behind the technology.
From Silicon Valley to India, Boston to Japan, here are some of the autonomous machine and robotic technologies powered by NVIDIA AI that are coming to the rescue in 2024.
Clearbot cleans up ocean trash
Clearbot, a Hong Kong and India-based member of the NVIDIA Inception program for cutting-edge startups, is making waves with its autonomous garbage boat powered by the NVIDIA Jetson platform for edge AI and robotics. .
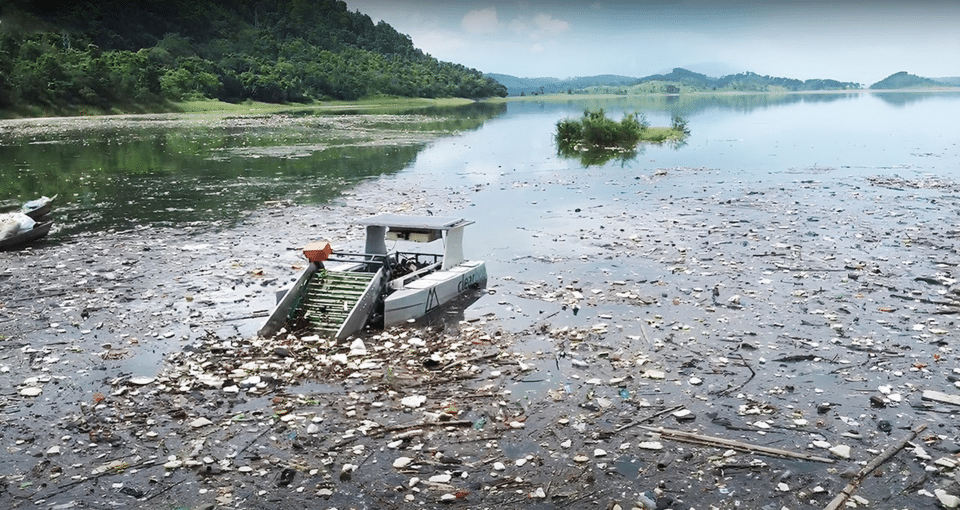

With plastic making up at least 85% of the world’s ocean waste, Clearbot aims to remove waste from waterways before it ends up in the ocean.
The company’s autonomous vessels are equipped with two cameras. One is for navigation and the other is for identifying waste scooped up by boats.
Clearbot used NVIDIA accelerated computing to train an AI model to identify trash and obstacles. Energy-efficient NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX System-on-Module allows battery-powered water purification boats to collect water for eight hours at a time.
The latest humanoid robot released as a figure
Silicon Valley-based Figure has announced Figure 02, a conversational humanoid robot that leverages the NVIDIA Omniverse platform and accelerated computing for fully autonomous tasks.
With a new human-scale hand, six RGB cameras, and a perceptual AI model trained on synthetic data generated with the NVIDIA Isaac Sim robot developer simulation platform, Figure 02 delivers the high-precision pick and place required for smart manufacturing applications. Can perform tasks.
The company recently tested Figure 02 on BMW Group’s Spartanburg, South Carolina, production line for data collection and use case training.
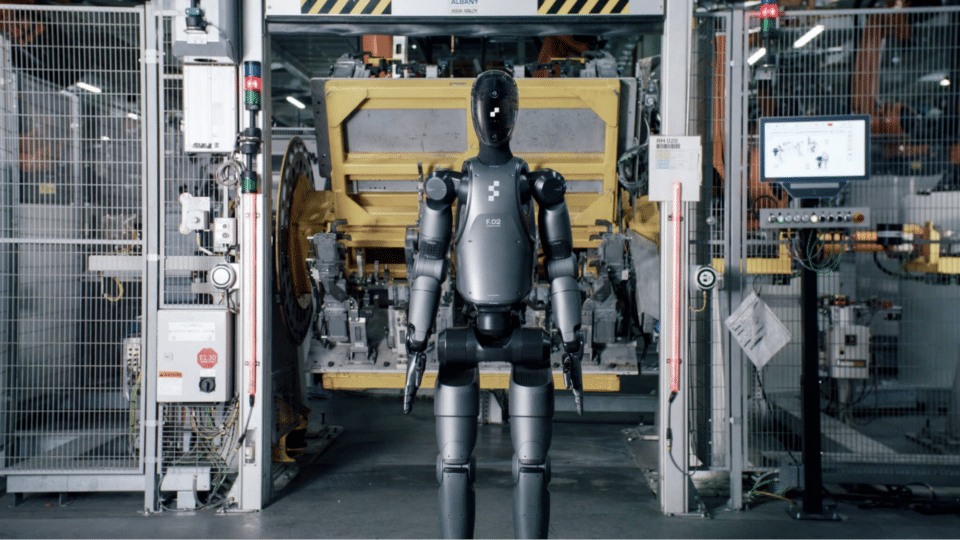
Figure is one of the first members to join the NVIDIA Humanoid Robot Developer Program, which is part of NVIDIA Inception and provides early access to advanced tools and computing technology for humanoid robot development. This includes the latest releases of NVIDIA Isaac Sim, Isaac Lab, NIM microservices, OSMO, Jetson Thor, and the Project GR00T general purpose humanoid foundation model.
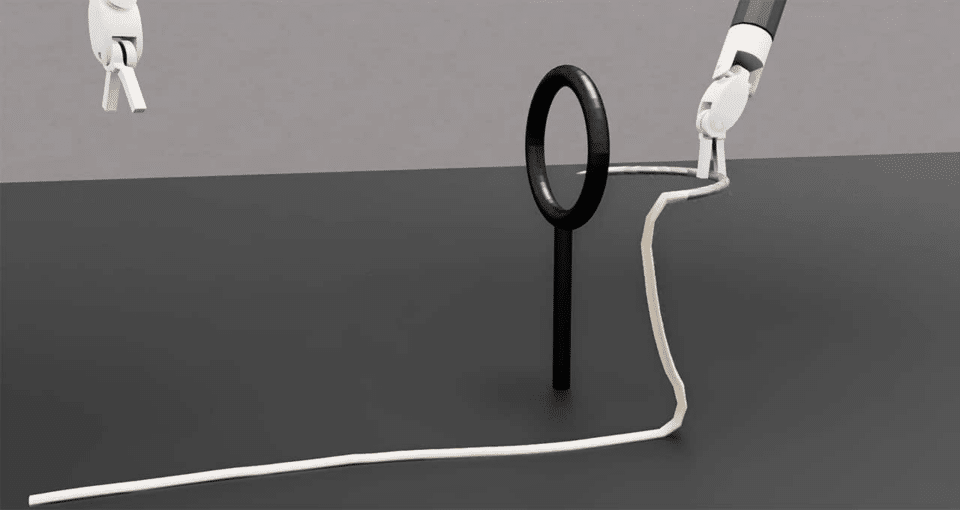
ORBIT – Surgical researchers prepare surgical robot
The ORBIT-Surgical simulation framework was developed by researchers at the University of Toronto, University of California, Berkeley, ETH Zurich, Georgia Institute of Technology, and NVIDIA. This will help train the robot, which can enhance the skills of the surgical team while reducing the cognitive load on the surgeon.
We support more than a dozen procedures inspired by minimally invasive surgery training curricula.
Needle locomotion robot research based on Isaac Sim and Omniverse, presented at this year’s ICRA Robotics Conference in Japan, also featured benchmarks for one-handed tasks such as picking up gauze, inserting shunts into blood vessels, and lifting. . Place the suture needle at a specific location.
Benchmarks also include two-handed tasks such as threading a threaded needle through a ring pole.
Zordi robot grows strawberries indoors
Zoldi, a Boston-based autonomous farming startup with farms in southern New Jersey and western New York, uses robotics to grow strawberries indoors.
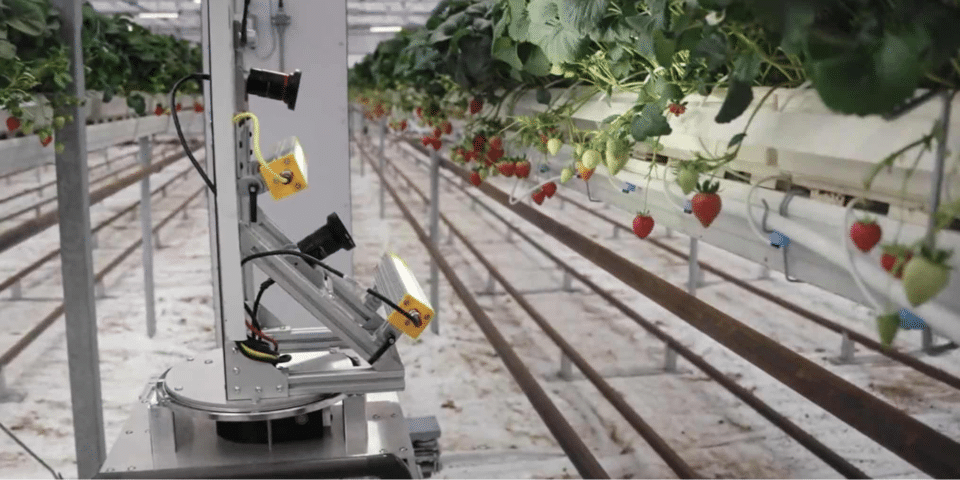

Autonomous greenhouse systems can support local markets around the world by reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation and providing fresher, better-tasting fruit grown more sustainably.
Zordi uses two types of robots within its operations. One is a scout robot that uses a foundational model to gather information about plant health, and the other is a harvester robot that carefully picks and places fruit and handles other tasks.
The startup is considering NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin modules to collect sensor data and run AI models.
Cutting-edge companies weren’t the only ones driving major advances in robotics this year. For example, high school and university students are developing robot guide dogs for the visually impaired and training robots to perform 1,000 chores.
Join NVIDIA at CES in Las Vegas from January 6th to 10th to learn more about the latest in generative AI and autonomous machines, including NVIDIA’s three-computer approach to robotics.

